WHAT IS
Correspondent Banking?
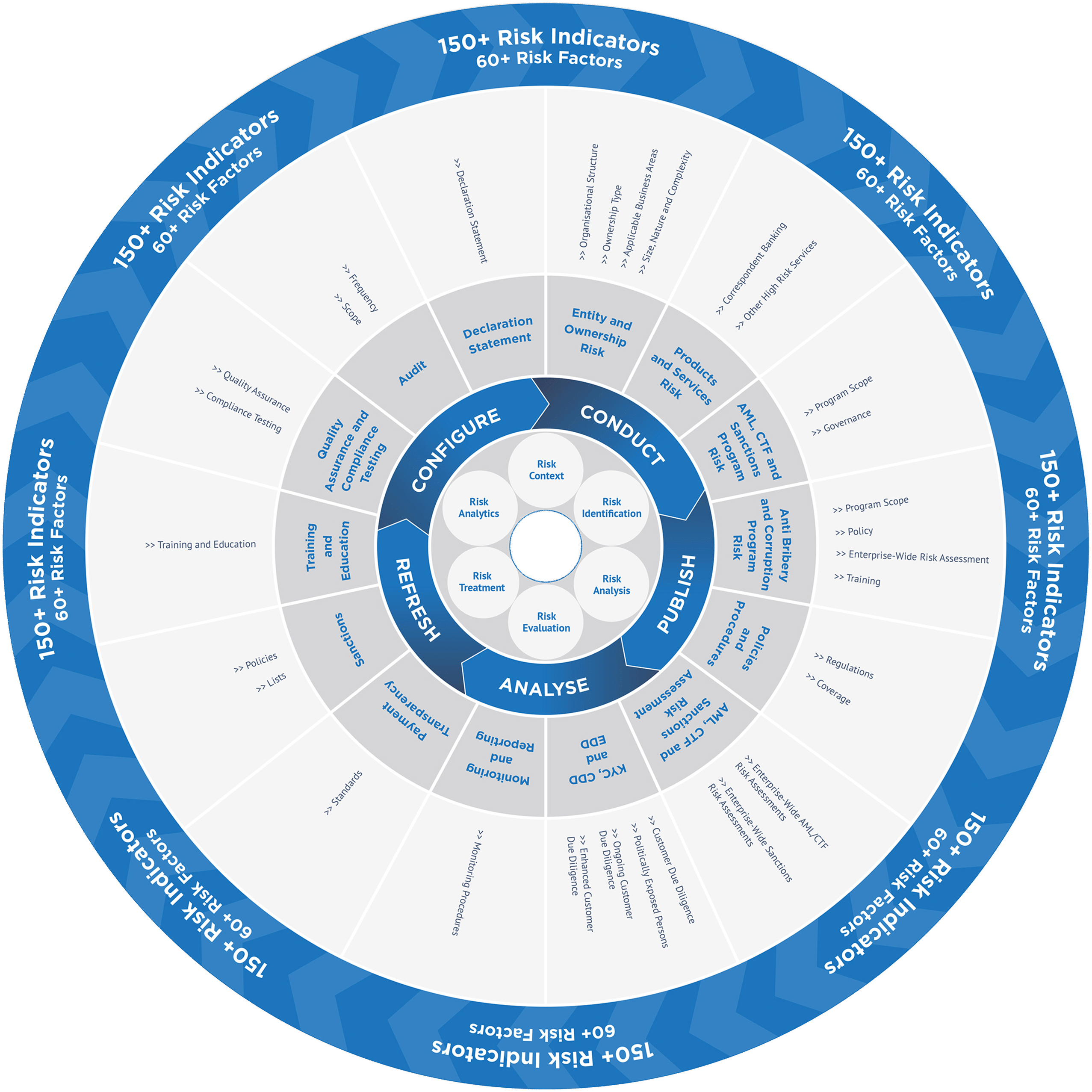
Correspondent banking is a financial arrangement between two banks, usually from different countries, where one bank (the correspondent bank) provides services on behalf of another bank (the respondent bank). These services often involve facilitating international transactions, processing payments, and managing foreign currency exchanges. Correspondent banking helps smaller or less established banks gain access to global financial networks and services, allowing them to conduct cross-border transactions and provide international banking services to their customers.
WHAT IS
Correspondent banking risk?
Correspondent banking risk refers to the potential dangers and challenges associated with the relationship between correspondent banks and respondent banks in the context of international financial transactions. These risks can arise due to various factors, including regulatory compliance, money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities.
One major concern is that correspondent banks may inadvertently facilitate the movement of funds for illegal purposes through their networks. As a result, banks that engage in correspondent banking need to implement robust due diligence procedures to ensure that the respondent banks they work with are not involved in any suspicious or illegal activities. Failure to adequately manage these risks can lead to reputational damage, legal repercussions, financial losses, and potential disruptions to the global financial system.
WHAT IS A
Correspondent Banking Risk Assessment?
A Correspondent Banking Risk Assessment is a process used by financial institutions, particularly correspondent banks, to evaluate the potential risks associated with their relationships with other banks, especially respondent banks, in the context of cross-border transactions. The purpose of this assessment is to identify and mitigate the various risks that could arise from these banking relationships, including money laundering, terrorist financing, sanctions violations, and other financial crimes.
The assessment involves analysing factors such as the regulatory environment in the respondent bank's country, the bank's financial stability, its anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing controls, and its reputation. By conducting such assessments, correspondent banks can make informed decisions about whether to establish or continue relationships with specific respondent banks and how to manage the associated risks effectively. This helps ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, prevent illicit financial activities, and maintain the integrity of the global financial system.
WHO MUST CONDUCT A
Correspondent Banking Risk Assessment?
Correspondent banking risk refers to the potential dangers and challenges associated with the relationship between correspondent banks and respondent banks in the context of international financial transactions. These risks can arise due to various factors, including regulatory compliance, money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities.
One major concern is that correspondent banks may inadvertently facilitate the movement of funds for illegal purposes through their networks. As a result, banks that engage in correspondent banking need to implement robust due diligence procedures to ensure that the respondent banks they work with are not involved in any suspicious or illegal activities. Failure to adequately manage these risks can lead to reputational damage, legal repercussions, financial losses, and potential disruptions to the global financial system.
WHAT RISK FACTORS SHOULD BE CONSIDERED WHEN CONDUCTING A
Correspondent Banking Risk Assessment?
When conducting a Correspondent Banking Risk Assessment, it's important to consider a variety of risk factors that could impact your relationships with respondent banks. These factors help you evaluate the potential risks associated with each relationship and determine appropriate risk mitigation measures. Here are some key risk factors to consider:
These risk factors should be assessed in combination to provide a comprehensive understanding of the risk profile of each correspondent banking relationship. Remember that risk assessments should be ongoing and regularly updated to reflect changes in the regulatory landscape, the respondent bank's operations, and other relevant factors.
Download our Correspondent Banking Risk Fact Sheet
Download our Correspondent Banking Risk and Control Module Brochure
Click on the button to download the Correspondent Banking Risk and Control Module Brochure
COMPLETE THE FORM
Access the Content Module Overview
The content module overview provides an introduction to correspondent banking and outlines the necessity and methods for its implementation.
Additionally, it presents the Arctic Intelligence Risk Assessment Platform, highlighting its potential advantages for your business.
Request your free copy now!