Designated services offered by
Legal Professionals
Under the AML/CTF Amendment Bill 2024, specific legal services will be designated as covered activities and will be subject to AML/CTF obligations. These services include:
By imposing AML/CTF obligations, authorities aim to prevent lawyers from being exploited as unwitting enablers of financial crime.
Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing (ML/TF)
Risks in the Legal Profession
Legal professionals face significant ML/TF risks, including:
- Misuse of Trust Accounts – Criminals may exploit lawyers’ trust accounts to layer illicit funds, making transactions appear legitimate
- Obscuring Beneficial Ownership – Legal professionals can be used to set up companies, trusts, and other structures that conceal the true ownership of assets
- Real Estate Transactions – Lawyers facilitating property purchases and sales may unknowingly assist in integrating illicit funds into the legal economy
- Third-Party Transactions – Criminals may use legal representatives to move funds through client accounts, distancing themselves from the money trail
- False or Fraudulent Legal Documentation – Legal instruments, contracts, and agreements may be manipulated to create a façade of legitimacy for illicit funds
- Cross-Border Transactions – International legal services may be used to transfer and layer illicit funds across jurisdictions with varying AML/CTF regulations
- Cash-Intensive Transactions – Handling large amounts of cash for legal services can be an indicator of money laundering
- Use of Legal Privilege to Shield Transactions – Criminals may attempt to exploit attorney-client privilege to prevent authorities from accessing suspicious financial dealings
- Facilitation of High-Risk Business Activities – Lawyers assisting with mergers, acquisitions, and complex financial deals may unknowingly enable money laundering
- Limited Awareness and Oversight – Without robust AML/CTF compliance, legal professionals may fail to identify or report suspicious activities, increasing the risk of facilitating financial crime.
To comply with the AML/CTF Act by 1 July 2026, legal professionals must conduct a thorough ML/TF risk assessment to identify, mitigate, and manage risks effectively.
For more information on the ML/TF risks faced by Legal Professionals click here.
AML/CTF
Programs and Policies
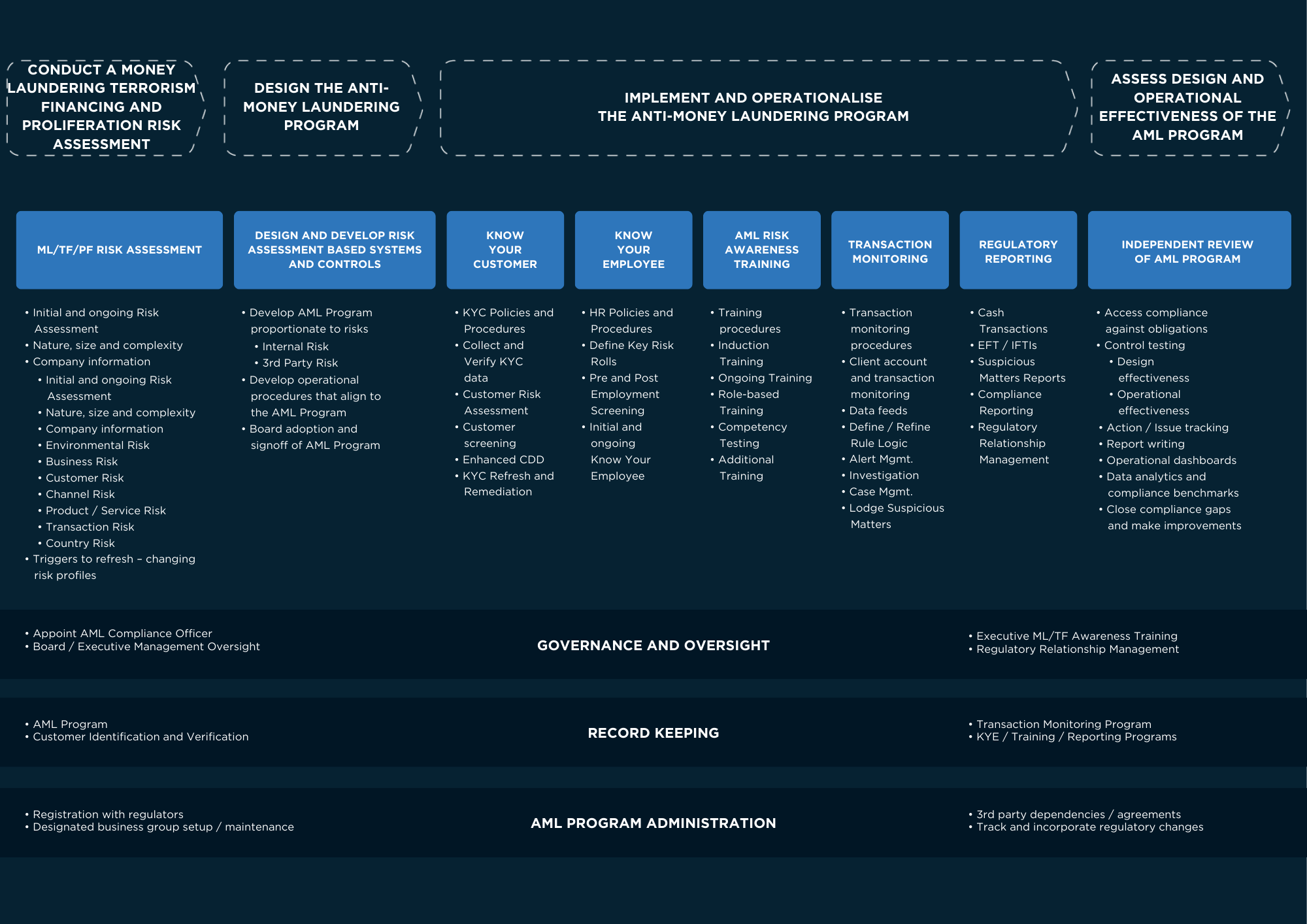
In addition to designing, executing and maintaining a money laundering, terrorism financing and proliferation financing (ML/TF/PF) risk assessment reporting entities are expected to implement AML/CTF policies that are both appropriate and proportionate to the identified risks, in order to mitigate and manage these risks.
The diagram below outlines at a high-level the other key pillars of an AML/CTF Program:
In addition to designing, executing and maintaining a money laundering, terrorism financing and proliferation financing (ML/TF/PF) risk assessment reporting entities are expected to implement AML/CTF policies that are both appropriate and proportionate to the identified risks, in order to mitigate and manage these risks.
In focus
Blogs
In focus
Whitepapers

Anti-Money Laundering 101: What do Australian Legal Professionals need to know about the AML/CTF Amendment Act 2024 and how can they start to prepare to comply?
Australian legal professionals must prepare for AML/CTF 2024 obligations and implement risk management measures.

How Do Organised Criminals Exploit Legal Professionals to Launder the Proceeds of Their Crimes and What Can You Do to Prevent This Happening in Your Business?
Criminals exploit legal professionals for laundering; strong compliance measures help prevent abuse.

Case Studies: How Organised Criminals Have Exploited Legal Professionals to Launder the Proceeds of Their Crimes and How You Can Prevent This Happening in Your Business
Case studies show criminals exploiting lawyers; strong compliance helps prevent money laundering.



