Designated services offered by
Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones
Under the AML/CTF Amendment Bill 2024, specific services provided by dealers in precious metals and stones will be designated as covered activities and will be subject to AML/CTF obligations. These services include:
If your business provides any of these services, it will be subject to AML/CTF obligations.
Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing (ML/TF)
Risks in the Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones sector
Dealers in precious metals and stones face significant ML/TF risks, including:
- High-Value, Portable Assets – Precious metals and stones can be easily transported and traded, making them ideal for laundering illicit funds across borders
- Use of Cash Transactions – Large cash purchases allow criminals to convert illicit funds into valuable assets without detection
- Smuggling and Cross-Border Transfers – Criminals exploit weaknesses in customs controls to move precious metals and stones internationally, avoiding financial scrutiny
- Refining Illicit Gold and Precious Metals – Dirty gold and other illegally sourced metals can be melted down and refined, erasing their criminal origins
- Trade-Based Money Laundering (TBML) – Over- or under-invoicing the value of transactions allows criminals to manipulate the movement of illicit funds
- Use of Intermediaries and Front Companies – Criminals may use third parties or shell companies to conduct transactions, concealing their identity and the true source of funds
- Collusion with Illicit Supply Chains – Stolen or illegally mined precious metals and stones can be introduced into the legal market, disguising their origins
- Multiple Resale Transactions – Repeated buying and selling of assets creates layers that obscure the money trail
- Lack of Customer Due Diligence (CDD) – Private sales and unregulated transactions make it difficult to verify the identity of buyers and sellers
- Use as a Store of Value for Criminal Proceeds – Precious metals and stones can be held indefinitely or used as collateral for loans, allowing criminals to retain wealth while avoiding detection.
To comply with the AML/CTF Act by 1 July 2026, dealers in precious metals and stones must conduct a thorough ML/TF risk assessment to identify, mitigate, and manage risks effectively.
For more information on the ML/TF risks faced by dealers in precious metals and stones, click here.
AML/CTF
Programs and Policies
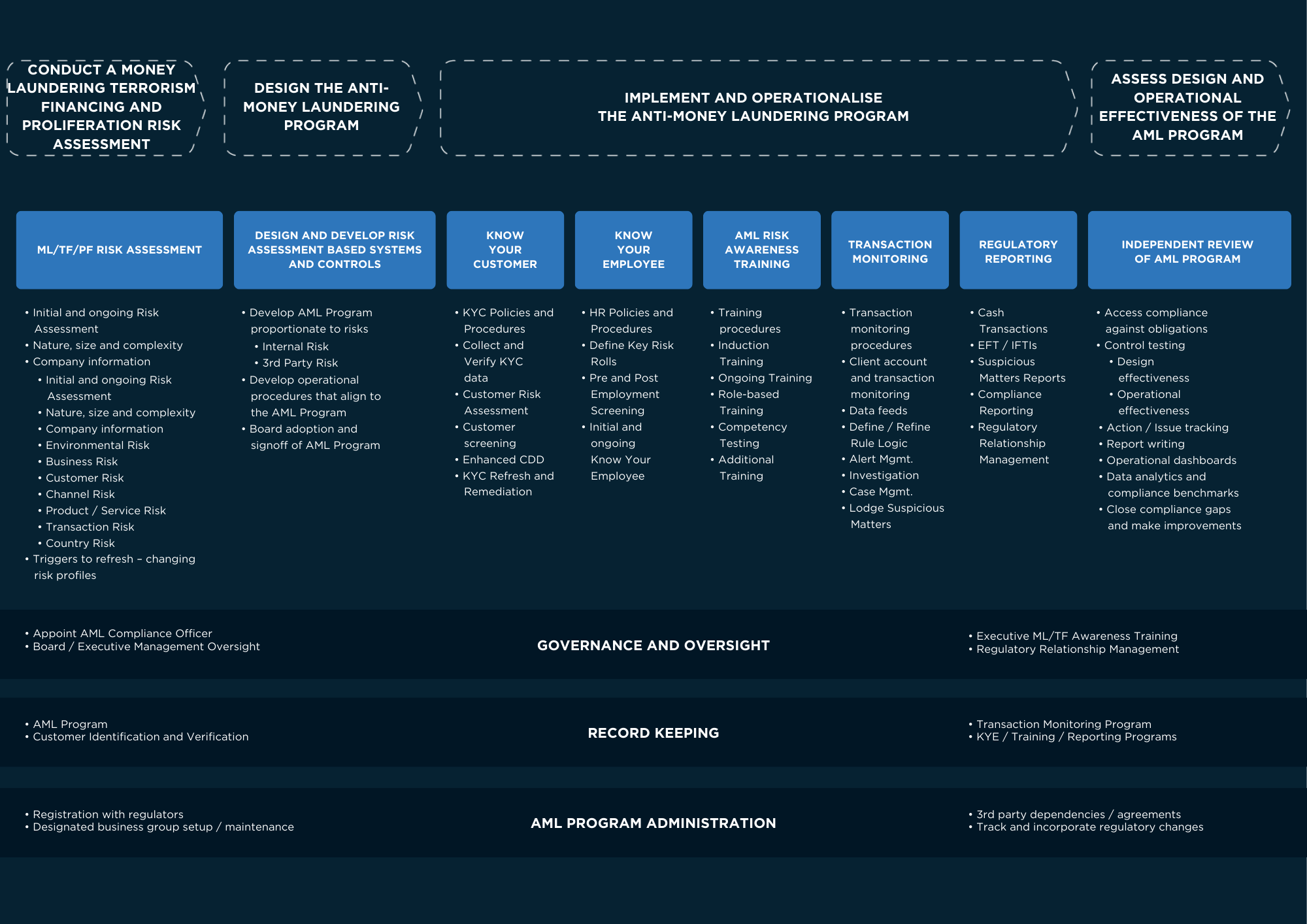
In addition to designing, executing and maintaining a money laundering, terrorism financing and proliferation financing (ML/TF/PF) risk assessment reporting entities are expected to implement AML/CTF policies that are both appropriate and proportionate to the identified risks, in order to mitigate and manage these risks.
The diagram below outlines at a high-level the other key pillars of an AML/CTF Program:
In addition to designing, executing and maintaining a money laundering, terrorism financing and proliferation financing (ML/TF/PF) risk assessment reporting entities are expected to implement AML/CTF policies that are both appropriate and proportionate to the identified risks, in order to mitigate and manage these risks.
In focus
Blogs
In focus
Whitepapers

Anti-Money Laundering 101: What do Australian Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones need to know about the AML/CTF Amendment Act 2024 and how can they start to prepare to comply?
AML/CTF compliance for precious metals dealers.

How do organised criminals exploit dealers in precious metals and stones to launder the proceeds of their crimes and what can you do to prevent this happening in your business?
Learn how criminals exploit precious metals dealers for money laundering.

Case Studies: How organised criminals have exploited dealers in precious metals and stones to launder the proceeds of their crimes and how you can prevent this happening in your business
Read about criminals exploiting precious metals dealers.



